
In an inverse manner, to convert dDm to milliwatts values you would use: You can convert milliwatts values to dBm using the formula: It makes it possible to express both very large and very small values in a short form: dBm is a unit of comparison and we use it to compare a signal to 1 milliwatt of power.

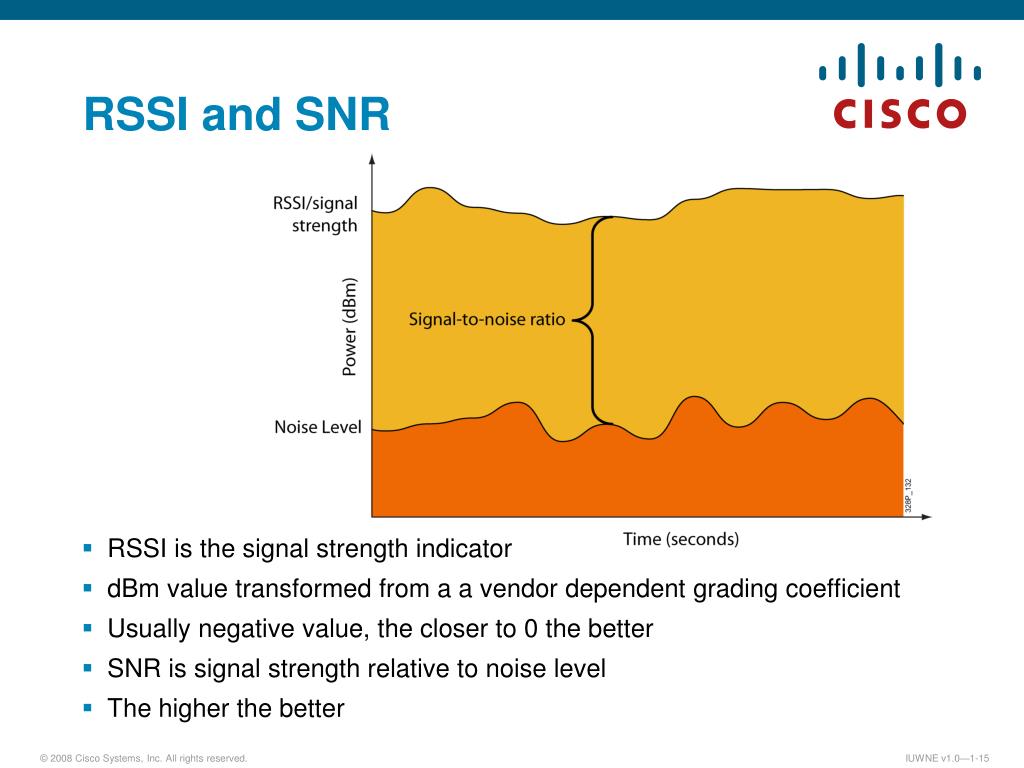
In fact, this is the reason we use dBm instead. Unfortunately, it is not how it works.īecause of physics and Isaac Newton’s Inverse-Square Law, signals attenuate very rapidly within just a few meters away from the transmitter and they will always measure below 1 mW at the receiver, making it impractical to use percentage values this way. So, if the AP is transmitting at 100 mW for example, 90% would mean the transmitted signal is being received at 90 mW, 80% at 80 mW, and so on. It should also help clarify why percentage values in WiFi Explorer might look so different when we compare them to the values we see in other tools.īefore we start discussing how the conversion works, let’s ask ourselves the following question: when we say that a network has 75% signal strength, what does that mean? Let’s assume for a moment that such value represents the percentage of transmitted power at which the signal is being received. The purpose of this blog is to describe this conversion process in WiFi Explorer. Its measurement depends on the receiving device.WiFi Explorer, as well as other wireless scanning tools, provides an option to display signal strength in dBm or percentage values. There is a point at which trying to obtain more signal delivers diminishing returns, because the quality of the connection is defined by more values than just RSSI (you will find more information on the other measurements in the Mobile Signal Strength Recommendations page). The closer to 0 dBm, the stronger the signal. However, -70 dBm and higher values usually equate to the modem being in an excellent coverage area. The exact numbers vary between cellular carriers. The higher the number, the better the signal. This value relates to the signal strength of the cellular signal from the tower to the modem. The RSSI is indicated by a negative dBm value. In telecommunications, Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) is a measurement of the power present in a received radio signal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
